After installing the new Windows 10, the user may encounter a situation where Explorer is missing one of the hard drives on which the necessary files are stored. This problem, of course, requires an immediate solution. In this article we will look at all the common causes of this problem and provide step-by-step guides to fixing it in each case.
Why the disk may disappear after installing Windows 10
Before you can determine the cause and fix the problem, you need to understand what type of problem you are experiencing. In particular, you need to find out what exactly disappeared: a logical partition on the hard drive (if there is only one hard drive, it is usually divided into partitions - system C: and user D:, although their number may be larger) or a separate hard drive ( if you have two physical drives installed on your computer). Most often, users deal with the first case.
Depending on the type of problem, its causes may be as follows:
- The hard drive cable is not tightly connected to the connector or has come loose. As a result, the system is simply unable to see the hard drive and show its contents. This reason is suitable for the second type of problem - the disappearance of an individual disk.
- The device experienced a random failure that caused damage to the logical structure of the hard drive partitions.
- The hard drive structure was damaged by malware that entered the computer.
- The partition letter on the hard drive has disappeared: it was not assigned when the OS was booted for the first time after installation. This may be caused by corruption of the file table or an error that occurred during installation.
- Logical block D: (or any other letter) was hidden by some user.
- A new, just purchased hard drive is connected to the system unit, which has not yet gone through the initialization and formatting procedures.
- Motherboard drivers need updating.
How to recover a missing drive on Windows 10
There are several ways out of a missing disk situation: from checking the physical connection to updating the motherboard drivers. Since it will not be possible to immediately determine the cause, it is necessary to act sequentially: apply method after method.
Checking the physical connection
If you have two separate physical drives, and the system does not find only one of them, you first need to check how tightly the cables connecting the hard drive and the motherboard are installed. Be sure to disconnect the PC from the electrical network and perform all manipulations with the device turned off.
If everything is fine with the connection, go to the BIOS and see if it sees the drive:
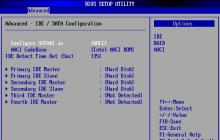
- Restart your computer: when the device starts booting, you need to have time to press the key that will take you to the BIOS menu. The keys vary depending on the model and manufacturer of your PC. Most often this is Escape, Delete, F2, F10 or F8. To go to the BIOS, press one of the buttons at the beginning of the PC boot: Escape, Delete, F2, F10 or F8
- When you are in the BIOS menu, in the Main tab, find the Primary IDE Master and Secondary IDE Master items if your hard drives are equipped with an IDE interface. If a set of BIOS mini-programs designed to test hardware components recognizes them at the moment, the drive description will include information about the manufacturer, model, and total memory capacity. It can also simply be Hard Disk. Which item to pay attention to, Secondary or Primary, depends on which connector on the system board the drive is connected to.
 Next to Primary IDE Master or Secondary IDE Master should be the name of your disk or the phrase Hard Disk
Next to Primary IDE Master or Secondary IDE Master should be the name of your disk or the phrase Hard Disk - If in the menu opposite one of the items there is Not detected, it means that the system did not detect it.
 If a partition is set to Not Detected, it means that the computer does not see the disk on this connector
If a partition is set to Not Detected, it means that the computer does not see the disk on this connector - If your hard drives have a SATA connection interface, look for items with this name and look at their meanings. The ports to which hard drives are connected should not display Not detected or Not Installed.
 Next to the SATA item corresponding to the connector to which the hard drive is connected, there should not be Not Installed or Not Detected
Next to the SATA item corresponding to the connector to which the hard drive is connected, there should not be Not Installed or Not Detected
If you do not find your drive that disappeared from Explorer in the BIOS, do the following:
- Check the quality of the connections of cables and cables again. Everything must be connected correctly, otherwise the system will not be able to detect the drive.
- Connect the hard drive to a different connector (perhaps the reason is that it is broken).
- Place the hard drive on another PC, if possible. This will ensure that it is not the problem.
If these steps do not produce results and the hard drive does not work on another device, take it to a service center for diagnostics. Perhaps it can be restored. Otherwise you will have to purchase a new one.
If the BIOS sees the installed drive, but it still does not appear in Explorer, move on to other methods of solving the problem.
Returning the old drive letter
If the reason for the disappearance is that the letter representing your local drive has “flown off,” you just need to return it or assign a new one in the Windows “Disk Management” system window:
- Press the key combination Win + R. This will open a small “Run” window, with which we will launch the “Disk Management” utility. Type or paste the previously copied command diskmgmt.msc into the input line. Then click OK or press the “Enter” key on your keyboard.
 Paste the command diskmgmt.msc into the "Open" field
Paste the command diskmgmt.msc into the "Open" field - The same window can be opened in another way. Click on the “This PC” icon with the right mouse button. In the context menu, select the “Management” item with the shield on the left.
 From the “This PC” context menu, select “Manage”
From the “This PC” context menu, select “Manage” - On the left side of the window, click on the “Disk Management” block - now you are in the desired window.
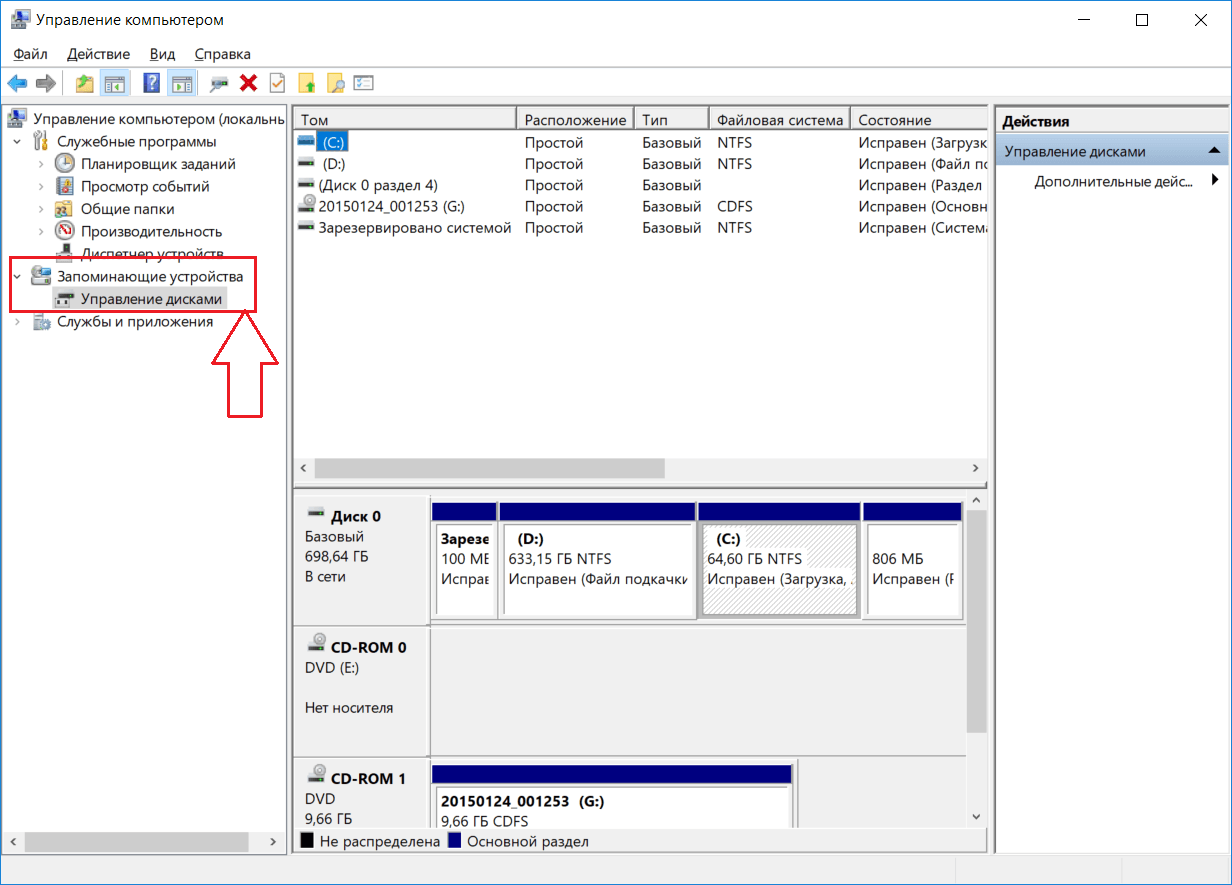 On the left side of the window, open the "Disk Management" section
On the left side of the window, open the "Disk Management" section - In the lower area of the window we find a drive without a name.
 At the bottom of the window, find the drive: if it does not have a name, assign a letter to it
At the bottom of the window, find the drive: if it does not have a name, assign a letter to it - Right-click on it and select the third item in the menu that opens - “Change drive letter.”
 Click on "Change drive letter or drive path"
Click on "Change drive letter or drive path" - Now in the small window, click on the “Add” button and select the desired letter of the English alphabet from the drop-down menu. To ensure that all changes are successfully saved, click on OK.
 Select a letter for your local drive
Select a letter for your local drive
Video: how to assign a letter to a missing local drive
Initialization and subsequent formatting in the Disk Management utility
This measure is suitable if in the Disk Management window your drive has one of two statuses: “No data” or “Not allocated”. In the first case, the procedure must begin with initialization. In the second, it is omitted - formatting is carried out immediately, that is, complete clearing of space for the future local disk. Let's look at the steps in detail in the instructions:
- Launch the Disk Management system window using one of the methods presented in the previous section of this article.
- In the lower area of the window, look for a drive labeled “No data.” Right-click on it. The "Initialize disk" option should be available in the context menu. Select it with the left button.
 Click on the “Initialize disk” item in the context menu
Click on the “Initialize disk” item in the context menu - In the next window, check the box to the left of the drive. Select GPT as the format if you want to work only in the “ten”. For other versions of Windows, MBR is suitable. Now click on OK and wait for the procedure to complete.
 Select a drive and partition style, and then click OK
Select a drive and partition style, and then click OK - Proceed to the second stage - formatting. It should be noted that if the disk was marked “Unallocated”, you should omit the initialization and immediately start formatting.
- Right-click on the drive again. In the menu that appears, select the “Create simple volume” option.
 Click on the option “Create a simple volume”
Click on the option “Create a simple volume” - Select a letter for the future local drive from the available ones and click “Next”.
 Select your local drive letter from the drop-down menu
Select your local drive letter from the drop-down menu - In the next window, set the format (NTFS is best) and the disk size. If you don't write it, the disk will be completely formatted and take up all the free space.
- Start the formatting process and wait until it finishes.
Format and restore on the command line
Complete cleaning and subsequent restoration of the local partition is possible in the classic Windows console “Command Prompt”. The method is quite complicated, so beginners are strongly advised not to use it.. However, if you are a confident PC user and have previously executed various commands in this editor, use the following instructions:
- First, let's launch the command line with administrator rights. To do this, click on the “magnifying glass” icon to the right of the “Start” button on the “Taskbar”. Type cmd in the field and find the cmd.exe file in the search results. Right-click on it and select “Run as administrator” from the menu that appears.
 Click on the line “Run as administrator”
Click on the line “Run as administrator” - Click “Yes” to allow Command Prompt to make changes to your computer.
 Click Yes to allow Command Prompt to make changes to your PC
Click Yes to allow Command Prompt to make changes to your PC - In the editor on a black background we will enter several codes one by one. When writing, you need to be extremely careful to avoid mistakes. After entering each code, you need to press the Enter button on the keyboard. First we print diskpart.
 Type the command diskpart and press Enter
Type the command diskpart and press Enter - We wait a few seconds. After that we write list disk. A list of currently connected drives will appear in the editor.
 We print the code list disk and look at the disk number
We print the code list disk and look at the disk number - Now we print select disk N, where N is the disk number in the list that we opened using the list disk code in the previous step.
 Type the command select disk N, where N is the disk number
Type the command select disk N, where N is the disk number - To delete the entire contents of this disk, enter the word clean. We are waiting for the cleaning procedure to complete.
 Enter the clean command to format the missing drive
Enter the clean command to format the missing drive - When the disk is formatted, you need to create a new local partition using the create partition primary code.
- Convert the disk to NTFS format using the format fs=ntfs quick command. We wait some time until the procedure is completed.
 Enter the command format fs=ntfs quick to set NTFS as the disk format
Enter the command format fs=ntfs quick to set NTFS as the disk format - We name the partition with an English letter: type the code assign letter=G, where G is the letter that you want to assign to the disk. It should not match the names of other local drives on the PC.
 Paste the command assign letter=G, where G is the local drive letter
Paste the command assign letter=G, where G is the local drive letter - Exit diskpart using a simple exit code.
Unhiding empty volumes
After installing the OS, the user's D: drive is usually empty. An option may have been enabled during Windows installation that allows you to remove empty drives from the list in Explorer. To turn off this feature, do the following:
- Launch the Windows Explorer startup window, which will display all currently available drives. In the upper area of the window, go to the “View” tab - an additional panel will appear. Find the “Options” button on it and click it with the left mouse button.
 In Explorer, find the Options icon in the View tab.
In Explorer, find the Options icon in the View tab. - From the drop-down menu, select “Change folder and search options.”
 Click on “Change folder and search options” to open an additional window
Click on “Change folder and search options” to open an additional window - Switch to the View tab and look for the Hide Empty Drives option. Make sure there is no check mark to the left of it. If there is one, remove it.
 Uncheck "Hide empty drives"
Uncheck "Hide empty drives" - To save all changes, click “Apply” and then OK to close the additional window.
If you have enabled the described option, as a result you will see in Explorer the previously missing local disk.
Motherboard driver update
The system may be unable to recognize the local drive if the motherboard lacks important updates to function. You can update your computer’s hardware in the standard “Device Manager” window:
- The easiest way to launch the “Device Manager” window is through the “Search” panel: click on the magnifying glass on the “Taskbar” and enter the appropriate query. When you start typing the second word, the system will immediately determine which window you want to open and give the desired result. We launch the system service by double clicking.
 In the search bar, enter the query "device manager"
In the search bar, enter the query "device manager" - In the window, look for the “System devices” object. Let's expand it: here we are interested in items with the word Chipset.
 Expand "System devices"
Expand "System devices" - Right-click on the first one and select the “Update driver” option in the context menu.
 Click on “Driver Update” in the context menu
Click on “Driver Update” in the context menu - In the new window, click on the link to start an automatic search for an available update.
 Click on the link “Automatically search for updated drivers”
Click on the link “Automatically search for updated drivers” - We are waiting for the search to complete.
 Wait while the system finds available updates for you
Wait while the system finds available updates for you - As a result, the system will either install the received update or inform you that the latest drivers are already on your PC.
 Click on “Close” to remove the additional window
Click on “Close” to remove the additional window - Automatic search cannot always find updates, so for a final check we again click on the “Update driver” option and this time select manual search on the PC. On the next page, click on “Select from the list of available on the device.”
 Click on the link “Select a driver from the list of available on the device”
Click on the link “Select a driver from the list of available on the device” - Select the item with Intel Chipset with the left mouse button and click “Next”. Now you need to wait again for the system to install the required update, if available.
 Select your motherboard model and click Next
Select your motherboard model and click Next - As a result, a message will appear indicating that the driver installation was successful. We repeat the procedure for all other items in the “System devices” section, the names of which contain the word Chipset.
 The system will notify you when it finishes updating the motherboard driver
The system will notify you when it finishes updating the motherboard driver - We close all windows and restart the PC so that all changes in the system take effect.
- After rebooting, check for the missing hard drive in Explorer.
You can update your motherboard drivers by manually downloading the update package on the computer developer’s website or the motherboard itself. Let's look at the procedure using the ASUS X555UB laptop as an example:
- Let's go to the official ASUS website, where we will find drivers for the X555UB model. At the top of the site, click on the “Support” tab.
 Click on the "Support" tab in the upper right corner of the page
Click on the "Support" tab in the upper right corner of the page - On the next page, switch to the “Drivers and Utilities” section.
 Go to the Drivers and Utilities tab
Go to the Drivers and Utilities tab - Now in the drop-down menu we need to select Windows 10 as the operating system - it is installed by default on the laptop of this model. Drivers are suitable in this case only for the “ten”. If you have a different version, you will have to look for drivers on third-party resources. When choosing a site, remember about computer security - trust only trusted ones.
 Select your operating system from the drop-down menu
Select your operating system from the drop-down menu - We scroll through the list of drivers for this device that appears: we need to find the Chipset item. Having found it, click on the blue “Download” button.
 Click on the “Download” button to download drivers for Chipset
Click on the “Download” button to download drivers for Chipset - The archive with the motherboard driver will be downloaded. We launch it and double-click the installation file with the exe extension. Close all currently active windows on the computer and click “Next”.
 Click "Next" in the initial window of the driver installer
Click "Next" in the initial window of the driver installer - On the next installer page, click “Accept”.
 Click on the "Accept" button
Click on the "Accept" button - We start the installation using the appropriate button. The installer will install the required driver. Then we reboot the system and check if the local disk appears in Explorer.
 Click on the “Install” button to begin installing the motherboard driver
Click on the “Install” button to begin installing the motherboard driver
Video: what to do if the system does not see the hard drive
The disappearance of a hard drive from the main Explorer window can be explained in different ways: physical failure of the media, poor connection of cables inside the PC, an error in assigning a letter when the OS is first started, lack of updates, etc. To solve the problem, you need to try method after method, since you will not be able to determine the cause right away.
The disappearance of a logical partition or a newly installed hard drive on a computer is not the most pleasant situation. This is understandable, because important user information could be stored in the same logical partition, which is not affected even when the operating system is reinstalled (naturally, if the installation is performed on the same system partition where the faulty or outdated OS is or was located). But let's see what can be done if the “D” drive suddenly disappeared (we are not considering the system drive, since if it disappeared, the operating system would not boot at all).
Reasons why a disk or logical partition disappears
As for the reasons for this phenomenon, they can be associated with both banal jokes and serious failures in the system itself. If we talk specifically about jokes, there are quite a lot of cases when a user opens “My Computer” and does not see a logical partition in it only because friends have set the attribute to hidden for the “D” drive. In this case, it is enough to remove it, and the section will become visible again. But most often, most experts name the following as the main reasons for the disappearance of a section:
- hardware problems (loose or incorrect connection of the new hard drive if it is used as a second);
- lack of initialization of the new hard drive;
- incorrectly specified letters and paths to logical partitions;
- reinstalling the system with the appearance of an unallocated area;
- changing the file system to an unreadable RAW format due to software and hardware failures;
- exposure to viruses.
Hardware check
Problems associated with incorrect or loose connections are almost the most common. In this case, it does not matter at all whether this applies to the main hard drive or to the second installed disk when creating a RAID array. To eliminate such problems, as is already clear, you need to check all connections, including the power supply. Just in case, you can check the functionality of the new hard drive by connecting it to another computer terminal. if it is not detected in this case, we take further steps.
Disk “D” is missing: how to get it back in the simplest way?
But usually, many problems of this kind arise due to incorrect settings of the operating system itself, which could be violated due to some short-term failures. So, for example, through “My Computer”, opening the contents of “Explorer”, the user can observe that the list of disks displays an empty element for which neither a letter nor a label (volume name) is set.
In this situation, the solution looks very simple. It is enough to call the disk management partition (diskmgmt.msc), through RMB on an empty space with a size corresponding to the missing partition, select the option to change the letter or path to the disk, and then assign a new letter. Please immediately note that you need to install either the letter “D” (if it’s a disk or a logical partition), or the letters of the English alphabet from “G” onwards, since usually “E” is reserved for a disk drive, and “F” corresponds to removable USB devices or cards memory. If you assign one of these letters to a logical partition, it is not a fact that other devices will be detected by the system when connected.
What to do if the “D” drive disappeared after reinstalling Windows?
Another common problem is a complete reinstallation of the operating system. Let's assume that the "D" drive on the computer disappeared just after performing such actions. What could this be connected with? Yes, only because the partition for installation was selected incorrectly, the partitioning was incorrect, etc. During the system installation process, disks and partitions are not displayed in the usual form, but are marked with numbers! You can eliminate such a nuisance by applying the solution described above, but only if the missing partition in the system is visible as empty space.

If this is an unallocated area, in the disk management section via RMB, you should select to launch the “Create a Simple Volume Wizard” on it and follow its instructions. At one stage, the disk will be assigned a letter, after which it will be proposed to format the partition, which is not advisable to refuse.
If we are talking about the fact that the “D” drive has disappeared in the form of a second hard drive, and not a logical partition, it is quite possible that it was not initially formatted or even initialized. In other words, the operating system does not see this device only because it does not have a file system.

In this situation, you can again use the disk management section, find the unallocated area, initialize the disk by selecting the appropriate item in the RMB menu, and then, as in the previous case, create a simple volume.
Note: if the “D” drive, installed as a second “hardware” device, has disappeared, the above operations can also be performed through the command console, but for ease of use, the standard system tools, accessed through the graphical interface, will be sufficient for the average user.
Sometimes the system partition may use the NTFS file system, but the logical partition uses FAT32. For the system to see it, you need to format it or convert it to NTFS.
Restoring a logical partition using special programs
Now let's look at the situation related to the logical partitions on which important user files were saved.

In this case, the partition can be recovered with the Recovery Expert tool, which is available in the Disk Director program from Acronis. Having launched the appropriate “Wizard”, you need to select the manual recovery method, set the full search type and wait until the restoration of the missing partition is completed, after which, by opening “Explorer”, make sure that all the information present in the partition is safe and sound.

Note: in some ways, this is also similar to working with an unallocated area.
Actions with RAW format
Finally, it happens that the “D” drive is not literally missing. It's just that its format has been changed to RAW, which is unreadable, which is why access to it may be blocked or limited. In this case, all the described methods are suitable. If possible, try formatting the partition or reinitializing it. If some information was stored in the partition, try restoring it using the specified utility or similar programs. Sometimes you can first make the files visible, again using third-party software, copy them to another location, and then perform a full formatting.
There are situations when, after installing, updating, or simply crashing, the Windows OS on your computer may disappear D drive display. Physically, he is still in his place, but the system refuses to see him, and various ways to solve the problem do not help. What to do in such a situation? In this material, I will tell you what actions you need to take if the D drive is missing on Windows 7 and 10, I will list the reasons for this dysfunction, and also explain how to fix it.
When considering the causes of the problem, it is important, first of all, to decide what we are dealing with - the loss of logical partition D on the hard drive of your PC (when logical partitions C and D are located on the same hard drive), or the loss of hard drive D (when C and D in the system are separate hard drives).
Depending on the answer to the mentioned question, the reasons for the D drive display problem may be as follows:

How to fix the problem if “Disk D is missing”
There may be several methods for solving the problem of the missing D drive, which, again, depends on whether you have lost a logical partition on your hard drive or a separate physical drive. Let's consider the solution options in order.
Lost logical drive D
So, suppose you have a hard drive on which two logical partitions, C and D, quite traditionally coexist. One day, partition D simply disappeared. What needs to be done?
- Assign a letter to the missing logical partition. A fairly common reason for section D to go missing is that it has lost its identifying letter (in this case, “D”).
- To restore it, click on the “Start” button, enter in the search bar: diskmgmt.msc - and press enter.
- The disk management menu will open in front of you. If your missing disk appears in the list of disks, but does not have an identifying letter (in the “Volume” column on the left), then you need to give it such a letter.
- We click on the empty space in the “Volume” column to the left of our unidentified disk with the right mouse button, and in the menu that appears, select “Change drive letter or drive path.”

Select "Change drive letter..."
Then click on “Add”, then on “Assign a drive letter” (select, for example, “E”). After making these changes, click on “Ok”, the specified disk should become available for viewing in Explorer.
Use the program's functionality Acronis Disk Director (currently version 12 of the product is current). Download and install this tool, run it, and in the menu on the left, select to launch the Acronis Recovery Expert program, which is used to recover hard drives.

After launching this program, select the manual recovery mode and click on the unallocated space of the hard drive.

Then we decide on the search method (choose the fast method). The program will look for the missing disk and, quite likely, will find it. Click on this disk with the mouse, and then click on “Next”. The program will restore this disk, and the problem of the missing D disk on the computer will be solved.

Hard drive D is missing
If your HDD (SDD) under the letter D is not displayed in the system, first of all I recommend checking the connection density of the cables going to this hard drive (check the connection density both to the connectors of the hard drive and the motherboard).
- If everything is tightly connected, and, nevertheless, the disk is not displayed, then click on the “Start” button, enter diskmgmt.msc in the search bar and press enter.
- In the Disk Management window that opens, see if the connected (but not visible in the system) disk is displayed here.
- If it is not displayed, then the problem is with the hard drive itself (faulty), or one of the hard drive cables is not working normally (damaged, not tightly connected to the appropriate connector, and so on).
Disk D may be displayed, but have different statuses:

The disk will be initialized and will receive a status with the area “not allocated” (sometimes some area of the disk may initially have this status). Right-click again on this unallocated area and select “Create simple volume”, then assign it a letter, size, and file system type (NTFS).

Select “Create a simple volume”
After completing these operations, drive D should appear in the Windows Explorer display on your PC.
Video solution
If you have lost drive D on Windows 7 or 10, it is important, first of all, to determine the essence of the missing drive D (logical or physical), and, depending on this, use the tools I listed above. After restoring access to the disk, I recommend checking the system for a virus (for example, Dr.Web CureIt will help!) It is quite possible that the cause of this dysfunction was the malignant activity of virus programs.
In contact with
It is quite rare that a local disk with the letter “D” or “E” simply disappears. In this case, you should not take any action unless you are a professional.
Each incorrect action can increase the risk of data loss on the specified HDD partition. However, it is still possible to fix this problem. So, in order to restore a missing HDD partition, you will need Acronis Disk Director, preferably version 11.
Method #1:
- Go to the “Disk Management” section, where you can see the unallocated area in the HDD - this is the missing partition.
- Assign the drive letter “D” to the unallocated area, after which the missing disk should appear. Otherwise, read method #2.
Method #2:
If the first method did not help you, then this method should fix the problem. You will need the Acronis Recovery Expert program included with Acronis Disk Director 11.
1) Launch “Acronis Recovery Expert” from “Acronis Disk Director 11”.
4) Select unallocated space, then click “Next”. 
5) As a search method, select “Fast”. 
7) We wait while the recovery process takes place. 
9) Click “Continue”. 
You turn on the computer and partition D is missing, what should you do? The most important thing in this situation is not to panic and think through all your actions, because if you act rashly, you can lose all the data on the missing partition.
How to recover a missing D drive?
1. Right-click on the “my computer” icon and open the “Manage” menu.
2. In the left column of the Management menu, find Disk Management and open it.
3. In the right window, drives marked with letter values will be highlighted. If there is no letter value in place of drive D, you need to set it by right-clicking on the drive without a value and selecting the “change drive letter” menu. Be careful, a 100 MB partition should not have a letter, this is the boot area of the operating system.
4. If drive D is marked as unallocated space, then we will need the Acronis Recovery Expert program, which is included in the Acronis Disk Director software package for working with disk spaces. You'll have to download this program.
5. Launch the Acronis Disk Director software package, find Recovery Expert on the left side of it and launch it.
6. Select manual recovery mode and click next
7. In the menu that appears, select unoccupied space and click next.

8. Then we will be asked to choose a search method; we are interested in a quick search.
9. The program will find information about drive D. You need to select it and click next.
10. The recovery process will begin, which may take some time. After the process is completed, you will see the result: Click next in this window. Then in the next window click continue.